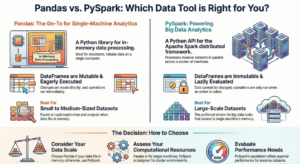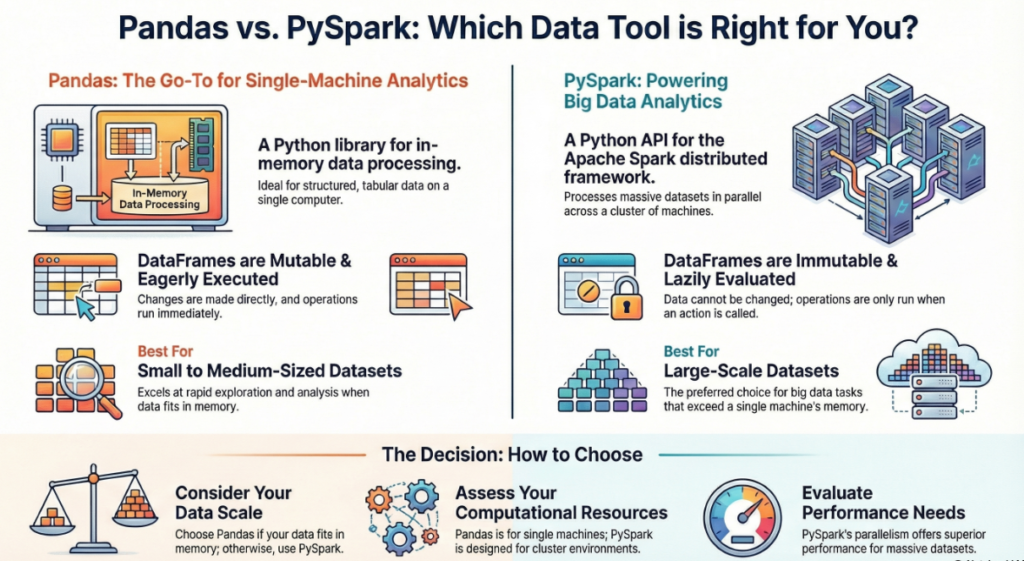
While both Pandas and PySpark provide DataFrame APIs for data manipulation, their syntax and execution models differ significantly due to their underlying architectures.
Core Execution Differences
• Execution Model: Pandas operations are eager, meaning they are executed immediately as they are called1. PySpark transformations are lazy, meaning they are not executed until an action (such as show() or count()) is called.
• Mutability: Pandas DataFrames are mutable1. In contrast, PySpark DataFrames are immutable and fault-tolerant; once created, they cannot be changed.
• Default Behavior: In Pandas, statistical functions are applied to each column by default without needing to specify the column name4. In PySpark, operations are distributed across a cluster, and you typically use the select() or agg() functions to target specific columns.
Syntax Comparison
| Feature | Pandas Syntax | PySpark Syntax |
| Import | import pandas as pd | from pyspark.sql import SparkSession |
| Creation | pd.DataFrame(data, columns=columns) | spark.createDataFrame(data, schema=columns) |
| Displaying Data | print(df) or df.head(n) | df.show() or df.printSchema() |
| Column Selection | df[['col1', 'col2']] | df.select("col1", "col2") |
| Filtering | df[df['age'] > 30] | df.filter(df['age'] > 30) |
| Adding Columns | df['new_col'] = df['old_col'] * 3 | df.withColumn("new_col", df['old_col'] * 3) |
| Aggregation | df.mean() (returns mean for all columns) | df.select(mean("age")) or df.groupBy("group").agg(mean("age")) |
| SQL Queries | Requires external libraries or methods. | Native support via spark.sql("SELECT * FROM table") after creating a temporary view. |
Statistical Functions and Transformations
Pandas includes a variety of built-in methods that work directly on the DataFrame object, such as df.corr(), df.median(), and df.std(). PySpark organizes these into specific transformations like groupBy(), orderBy(), and dropDuplicates(). To perform complex math in PySpark, you often need to import specific functions from pyspark.sql.functions (e.g., mean, col, max).
Conversion between Libraries
The sources note that you can convert between the two formats as needed:
• Pandas to PySpark: Use spark.createDataFrame(pandasDF) to leverage parallel processing on multiple machines.
• PySpark to Pandas: Use the .toPandas() method. However, this is an action that collects all data into the Spark Driver memory; if the dataset is too large, it will trigger an OutOfMemoryException.
——————————————————————————–